Numerous research findings and progresses have been obtained in forest protection against forest diseases, pests and forest fire and applied in practices.
Forest pest control
Technologies and systems have been developed in preventing and controlling Dendrolimus spp., bamboo locust, Hippota dorsalis, Matsucoccus matsumurae, pine shoot insects, Saperda calcarata, Apocheima cinerarius, Dendroctonus valens, Hyphantria cunea, Gilpinia lipuensis, pine wilt disease, poplar canker, paulownia witch’s broom disease, bacterial wilt of eucalyptus and etc. A shift from individual target control into integrated and ecological control was accomplished. Microorganisms and natural enemies were studied with priority. The Chinese Academy Forestry (CAF) has invented the first Bt pesticide in China and continuously developed and applied highly virulent bacteria strains.
Remote sensing and semiochemical approaches have been applied in monitoring the occurrences of pest disasters and the dynamics of targeted species. Long-term intensive research has been conducted for controlling Dendrolimus spp., identifying various typical zones of its occurrences, establishing serial forecasting and monitoring systems and applying integrated biological control which has been proved to be highly effective – the occurrences of Dendrolimus spp. in pilot areas were reduced by 90% or above. In particular, DCPV (Dendrolimus cytoplasmic polyhedrosis virus) is proved to work excellently in controlling Dendrolimus spp. Highly virulent nuclear polyhedrosis virus of Apocheima cinerarius has been obtained and new Aci-NPV technique has been developed, producing a 90%+ performance in in-forest application, where one-year application can generate effects for 3-5 years. Chouioia cunea, an effective natural enemy of Hyphantria cunea was found for the first time. The release of Chouioia cune and HC-NPV (nuclear polyhedrosis virus) can decrease the infected trees to below 0.1% in the testing areas. Such method has been applied in 2/3 of the area prone to be affected by Hyphantria cunea.
The application of Dastarcus helophoroides, a parasite natural enemy insect of longicorn can reduce the longicorn population by 86%. Bamboo pests were studied and the biological characteristics and occurring rules of 48 bamboo pests were clarified. Based on the bio-ecological characteristics, bamboo pest control methods were applied in a total area of more than 6,7000 ha in seven provinces and autonomous regions, showing an efficiency of 95% or above. The temporal sequence of dynamics of bamboo beetles has been disclosed and applicable food baits have been selected.
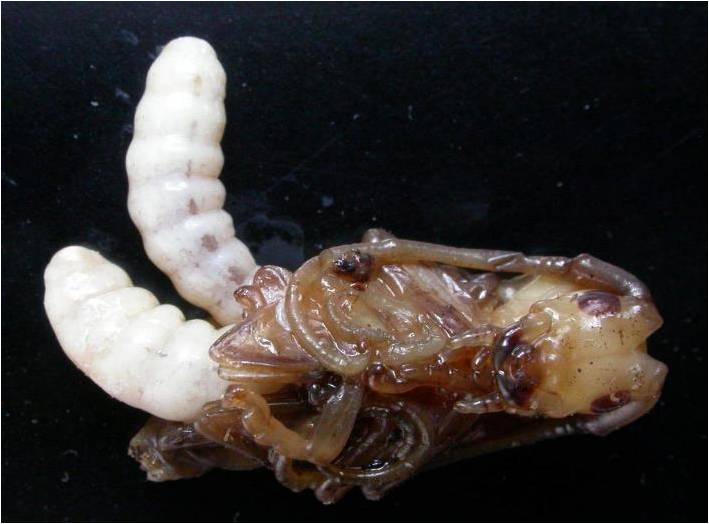
Larvas of Dastarcus helophoroides parasitizes longicorn
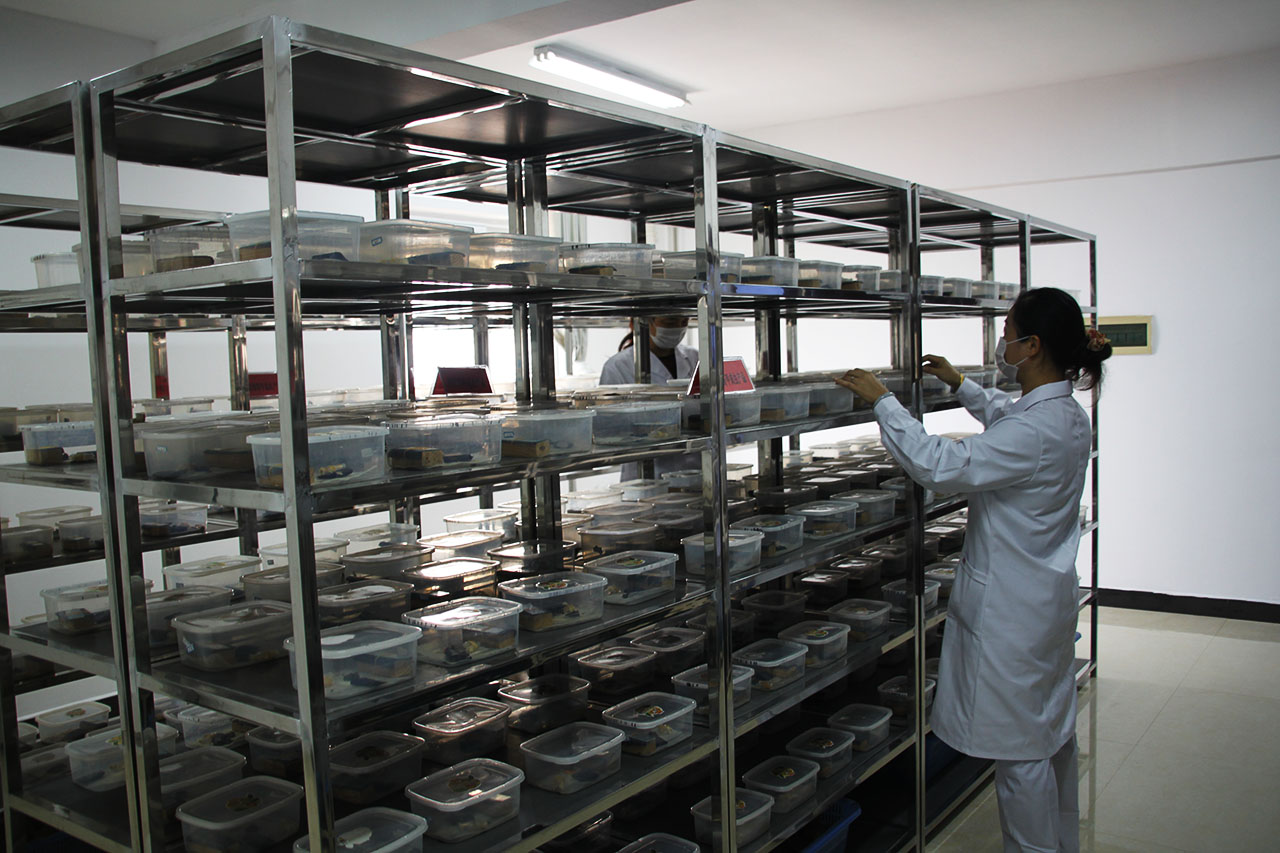

Dastarcus helophoroides Breeding
Genealogical classification and identification were carried out against some important pests, including sawflies, ants and nematodes, and a number of new genera and species of them have been published. Forest Insects of China, the most complete monograph of forest insects in China was published to introduce the morphology, biological characteristics and control methods of more than 800 forest insects. In recent years, the chemical-ecological control of Dendroctonus valens has been studied and obvious progress has been made.
Forest disease control
In term of forest diseases, poplar species resistant to canker were selected and used in forest production. The technology in removing MLO pathogens of paulownia withes broom disease using temperature treatment was created, which can achieve 100% detoxication. Early diagnosis methods of dangerous invasive diseases, such as pine wilt disease, have been developed and types of epidemic areas affected by pine wilt disease have been identified. These research findings have provided scientific evidence and methodologies for quarantining and detecting biological invasion.
Forest fire control
Breakthroughs were made in the fire resistance mechanism and establishment technology of green firebreaks. A database of fire-resistant tree species was established based on four categories of identification methods, i.e. determination, discriminant analysis, clustering analysis and multi-target decision-making of indicators of fire-resistant species. The county-level emergency commanding systems of forest fire fighting which integrates ground patrolling, public reporting, helicopter patrolling, satellite monitoring, etc., have been developed and applied. County-based early warning systems are also developed and applied, with hierarchic early-alarming technology studied, which realizes spreading simulation and early-alarming for fire-fighting under complex meteorological conditions, landforms and vegetation covers. Mechanism of fire starting and integrated control technology were studied and a database about occurrences and fighting of historically significant and severe fire disasters in the southwest and northeast was established.
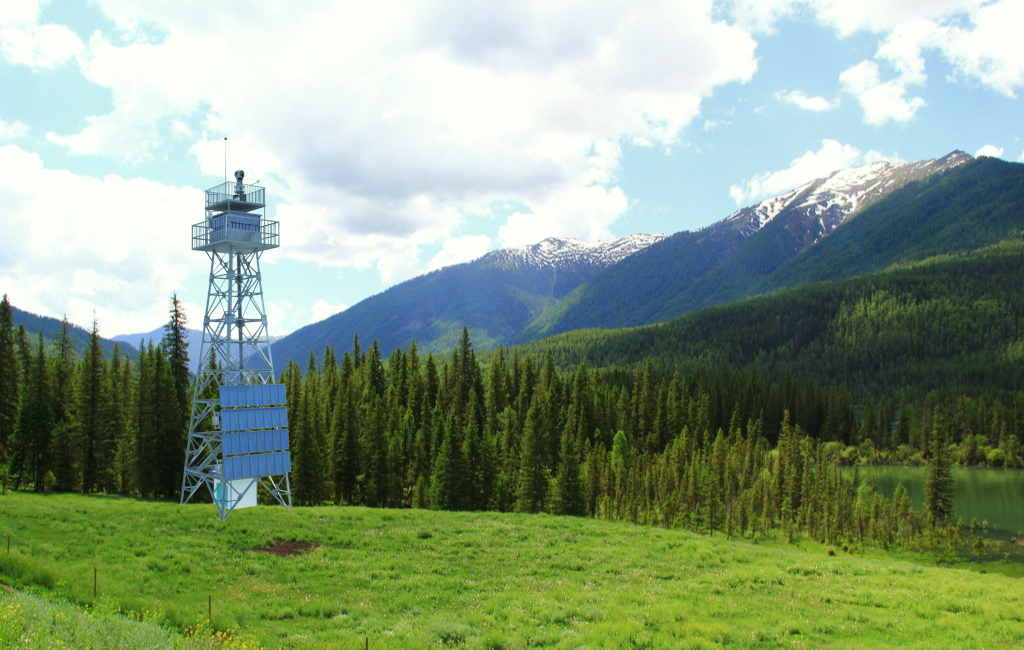

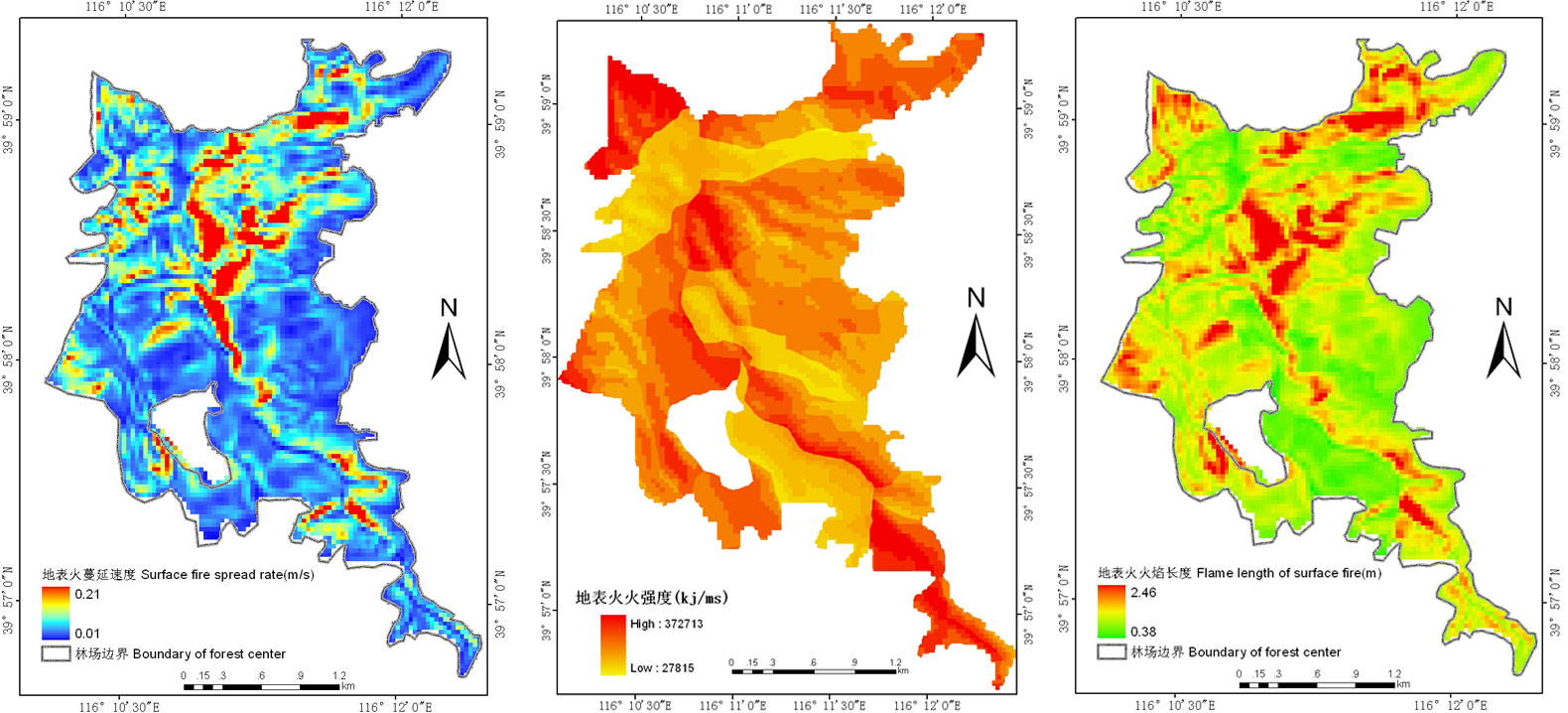
A county-level emergency commanding system of forest fire prevention