Remarkable research progresses have been made in forest cultivation, ecology of plantations, forest ecological programs, shelterbelts, forest ecosystem observation, and etc.
Natural forest protection and ecological restoration
The study of Chinese Academy of Forestry (CAF) on natural forest protection and ecological restoration has tackled the main technology issues in natural dynamic disturbances and conservation, restoration of typical degraded natural forests, landscape restoration and spatial management, etc., and presented a model of restoring degraded natural forests. In addition, eco-friendly harvest technology considering both the common technical standards and the appropriate technical mode for specific forest types was developed for logging and regenerating natural forests in northeast China.
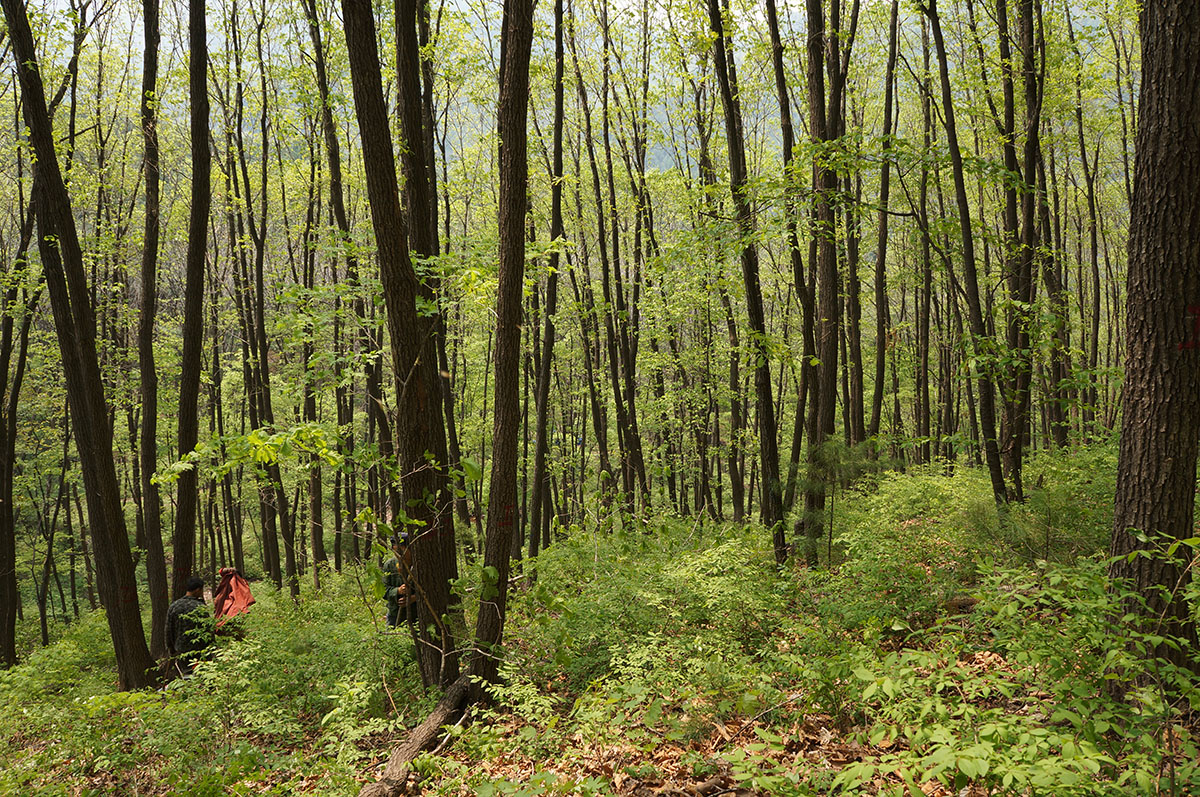

Regeneration by forest gap regulation and forest ecological tending operation in the mixed forests of deciduous broadleaved tree and Korean pine in northeast China
The Chinese Academy of Forestry is equipped with 36 field stations of terrestrial ecosystem research. A national ecosystem observatory network has been established within the research facilities and platforms of the Chinese Academy of Forestry. The long-term observation and research of tropical forest ecosystems in Jianfengling of Hainan Island, for the first time, disclosed the flow rules of water, nutrients and energy in tropical forests and clarified the structure, function and way of sustainable development of tropical forest ecosystems.
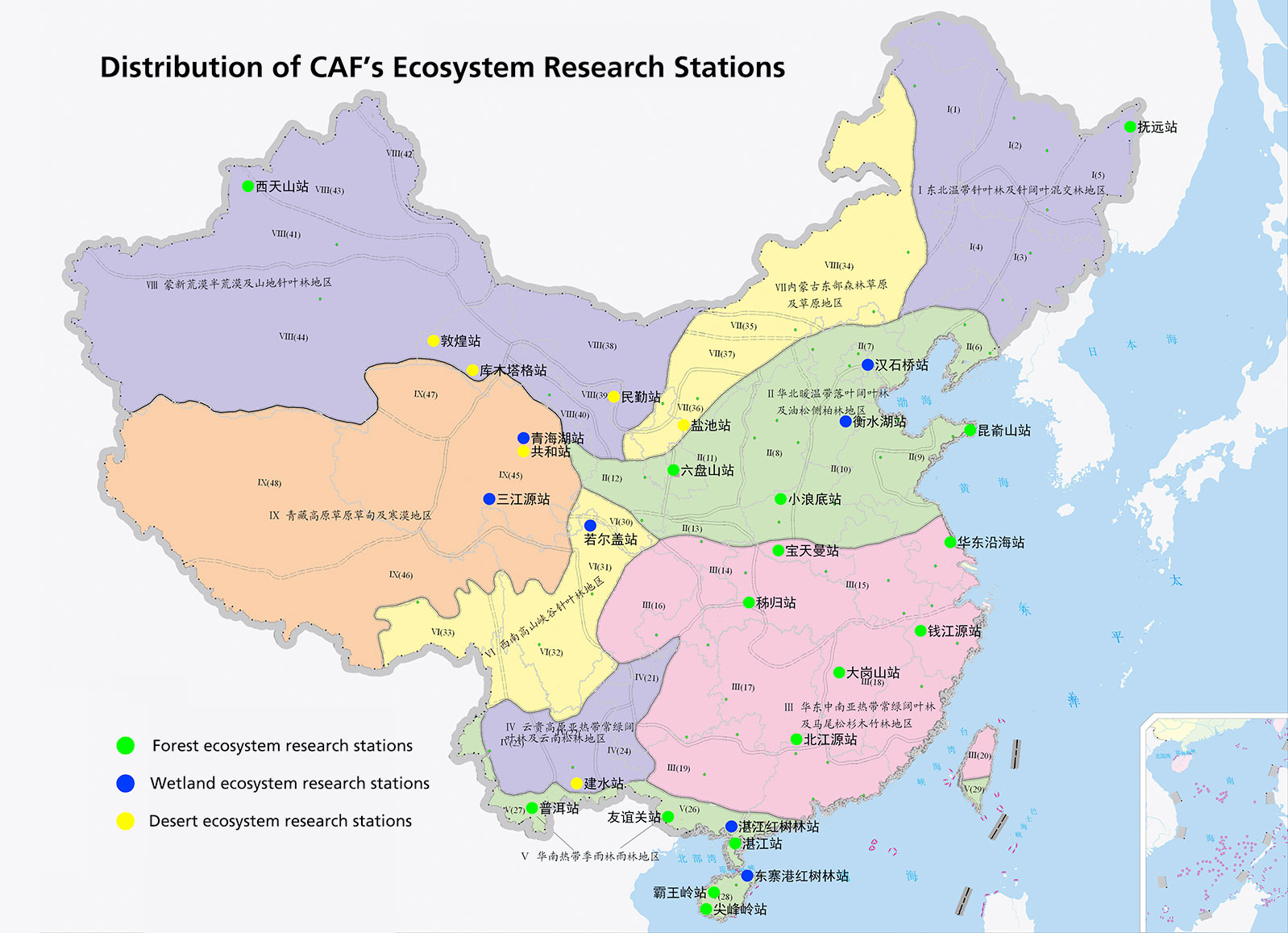
Distribution of CAF’s Ecosystem Research Stations
The long-term research of complex ecosystems in agricultural areas in Huanghuaihai Plain made breakthroughs in species disposition in ecosystems, exploitation of potential niches, water ecological characteristics, light utilization, etc., and provided a multi-species, multi-layer and multi-benefit agro-forestry model with spatial-temporal sequences, which helped increase the efficiencies of light and water utilization by 12% respectively and add agricultural yields by 18%, resulting in 28% extra benefits in comparison to ordinary farms.
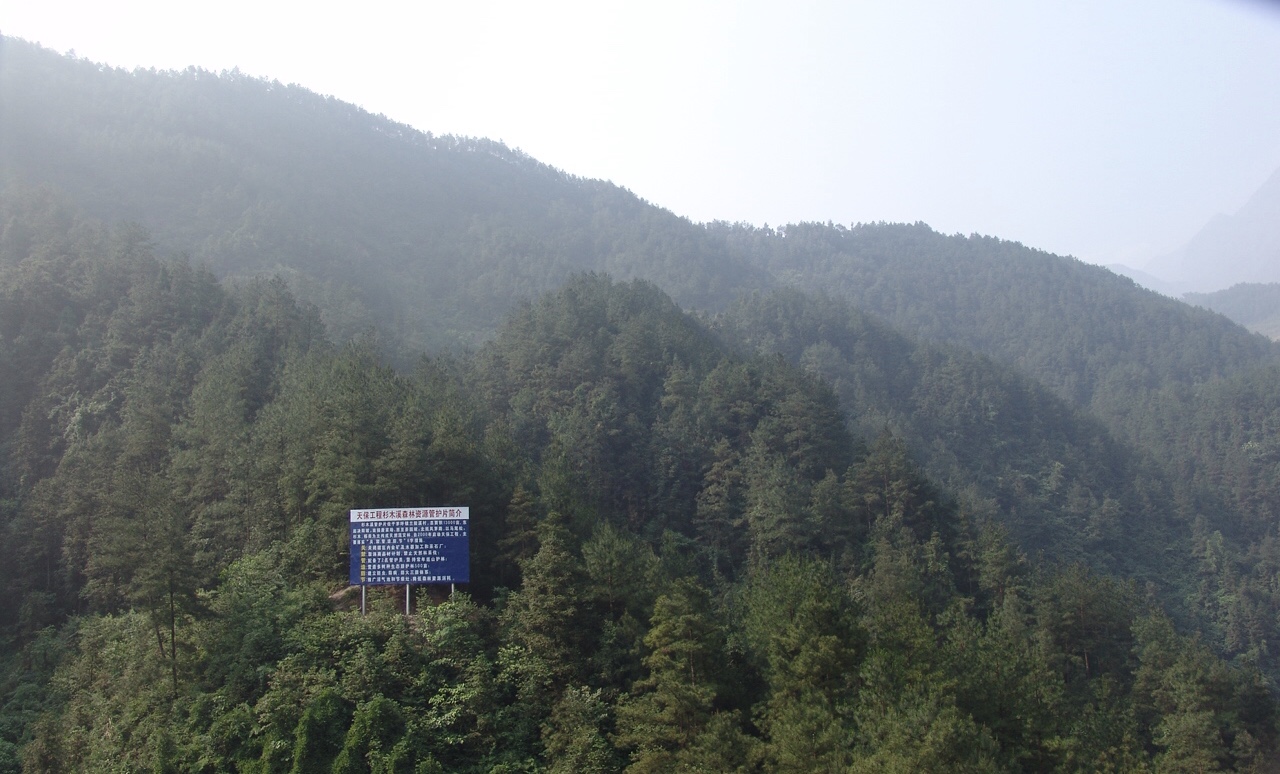

Efficient shelterbelt system in the Three Gorges area
Afforestation technology
Site-appropriate and species-appropriate afforestation technology developed by Chinese Academy of Forestry works well for the water and soil conservation in rocky hills of Taihang Mountain. Enclosed forest cultivation and artificial regeneration was applied against the rocky desertification in south China and underpinned the ecological rehabilitation of local Karst areas. Domestication and afforestation technology of mangrove species was studied and applied in coastal shoals in south China. Chinese Academy of Forestry has been researching on developing a state-appropriate forest ecosystem network to meet with the eco-security needs of national and local forest ecological program and has carried out pilot studies in 22 provinces and autonomous regions.
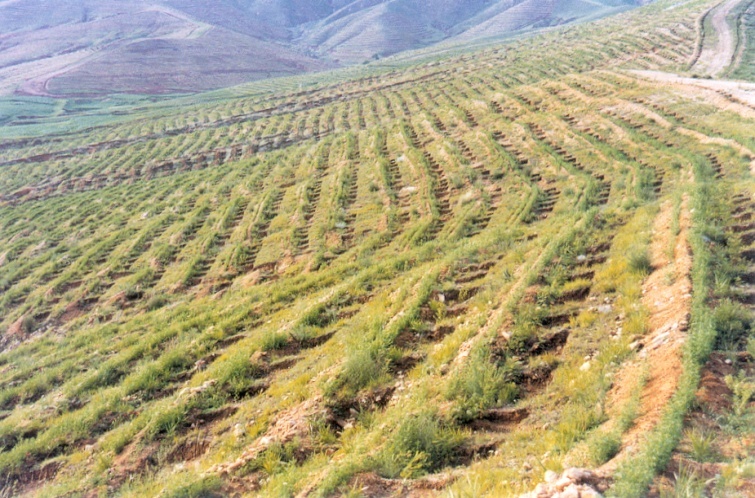

Afforestation in rocky hills of Taihang Mountain
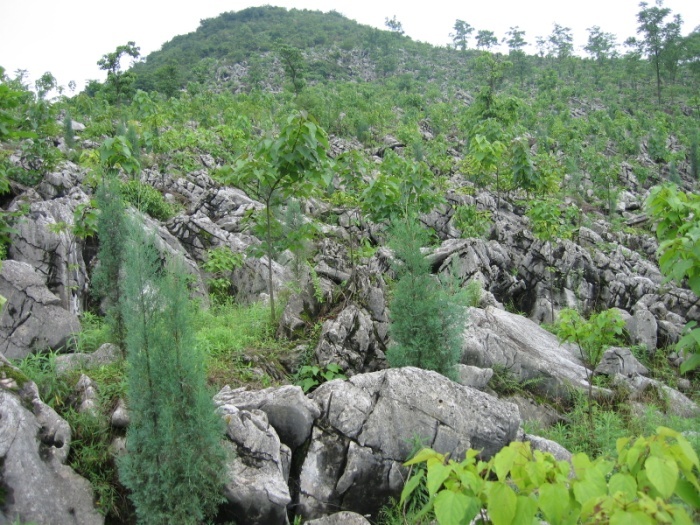

Afforestation in rocky desertification areas in south China
Forest ecology application
A national ecosystem observatory network has been established through its monitoring and evaluation of forest ecosystem functions, and the Criteria & Indicators of observation and assessment of China’s forest ecosystem services and functions have been provided. The project “China Forest Ecosystem Structure and Functioning Logic”, funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, initiated the application of long-term forest ecosystem observation to conduct the networking of inter-disciplinary ecosystem research. Outcomes generated through the ecosystem research by the Chinese Academy of Forestry include, but not limited to the identified geographical distribution of China’s diverse forest ecosystems and their composition of communities, productivity, nutrient cycles, eco-hydrology and energy use, the spatial variation of forest carbon stocks in China, the impacts of climate change on woody plants, methodology of carbon accounting and monitoring, the coupling mechanism of eco-hydrological processes, conservation of forest biodiversity, wetlands, birds and wildlife, etc.

Ruo’ergai alpine wetland in Sichuan Province